There are times when we want to extract data from a website. In most cases, you are provided with an API, but that’s not always plausible. So, when a website does not provide an API, the only way to get the data from the website is to scrape it off yourself.
In this tutorial, we are going to build a simple scraper using PHP to extract data from Wikipedia (I’d highly recommend you to use Wikipedia API over this. This is just for the tutorial purpose.) and another scraper that extracts Anna University result.

There are various external libraries such as Simple HTML DOM and cURL, which I highly recommend you to check out after this tutorial, but we are going to proceed with simple raw PHP.
Before you proceed, remember that Web Scraping is definitely a gray area. So, make sure you are not breaking terms and conditions of the site you are scraping the data off. This tutorial is just for educational purpose.
Simple Wikipedia Scraper
We are going to do this in 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the content
First, we have to pull the content off the Wikipedia page. For this, we use file_get_contents()
function, which is used to retrieve the content of a file using its URL. It takes in
a URL of a file and returns its content.
The above code returns the content of the Wikipedia page as a string which the browser interprets as something like this:
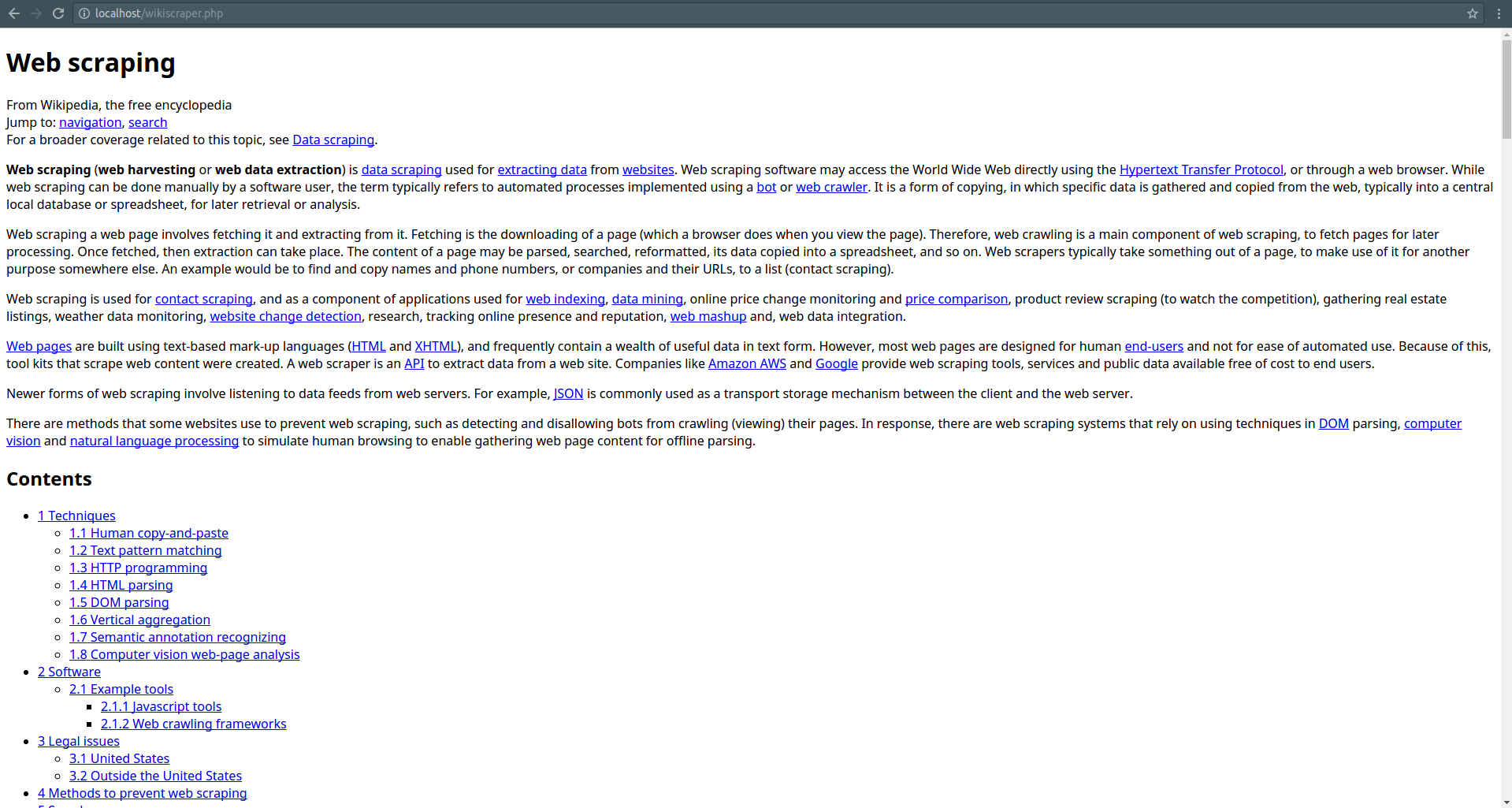
Step 2: Parse the string as DOM
DOM stands for Document Object Model.
It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed
and manipulated. In simple words, it generates a tree like structure to access the
data in it. It is used by the browser to parse HTML into displayable content.
$url can be converted to DOM using DOMDocument
class in PHP.
DOMDocument's constructor takes in XML version and encoding as parameters.
Don’t worry if you don’t know what they are, just use the line below:
$dom = new DOMDocument('1.0', 'UTF-8');
The loadHTML() method of
DOMDocument takes in the content and creates a DOM.
Note: If you’re new to PHP classes, they are very similar to the ones in C++ and Java.
The only difference you have to know to continue this tutorial is that PHP uses
-> instead of . to access class members.
Step 3: Scrape the data
This is the part where you have to use your brain. Since every website is not built
the same way, you have to know your way through the website’s structure. To do this,
just try going through the website’s source to determine the appropriate selectors
to crack into the data.
For example,
if you go through https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_scraping ’s
source, you can see that the title has an ID of #firstHeading.

We can retrieve a DOM Element with its ID using getElementById method. getElementById() method returns an object of DOMElement type.
The content inside a DOMElement is stored in nodeValue attribute.

Next, We’re going to extract the first paragraph of the Wikipedia page. Going
through the source again, we can see that the first paragraph is within a p tag
inside #mw-content-text.
getElementsByTagName
rerurns a DOMNodeList object,
which is a collection of DOMElement objects ordered, which can be accessed using
item() method.
In the example, the first paragraph is returned by item(0). Like how we did in
the title, we extract the text using nodeValue attribute.

That’s it! We have successfully scraped data off the Wikipedia page.
Try going through the documentation to get a clearer picture. If you find the documentation difficult, I’d recommend you to go with some library. If you have any problem following the tutorial, please do post it in the comments below.

The part 2 of this tutorial continues on a real world example of scraping the Anna University website for result into an excel file. If you liked this, please do check this out: Web Scraping 101: Anna University Result Scraper